Memorizing and Relearning
When previously acquired memories are recalled they can be updated with new information. During this process the memory becomes labile and susceptible to interference – and requires the activation of molecular and cellular mechanisms that mediate the reconsolidating of the memory trace. By contrast, if memories are repetitively retrieved without any reinforcement, they can be actively suppressed. This “extinction” of memories also represents an active process of memory modification.
Clarifying these processes is important, not only to better understand how we maintain and strengthen memories over live time, but also in order to develop new strategies for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder. We have identified involved neuronal circuits and cellular signals in the hippocampus.
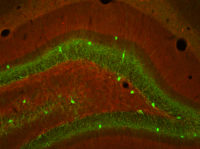
The image shows GABAergic interneurons (green cell bodies) in the dentate gyrus,
which are critical determinants for the strength and specificity of aversive
memories.
Selected publications
Çalışkan G, Müller I, Semtner M, Winkelmann A, Raza AS, Hollnagel JO, Rösler A, Heinemann U, Stork O, Meier JC. Identification of Parvalbumin Interneurons as Cellular Substrate of Fear Memory Persistence. Cereb Cortex. 2016 May;26(5):2325-40.
Šmidák R, Mayer RL, Bileck A, Gerner C, Mechtcheriakova D, Stork O, Lubec G, Li L. Quantitative proteomics reveals protein kinases and phosphatases in the individual phases of contextual fear conditioning in the C57BL/6J mouse. Behav Brain Res 2016 Apr 15;303:208-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.12.033.
Sase S, Sase A, Sialana FJ Jr, Gröger M, Bennett KL, Stork O, Lubec G, Li L. Individual phases of contextual fear conditioning differentially modulate dorsal and ventral hippocampal GluA1-3, GluN1-containing receptor complexes and subunits. Hippocampus, 2015 Apr 25. doi:10.1002/hipo.22470
Funding
Collaborative Research Center 1436, project A07: Orexinergic modulation of neural resources 
PIs: Prof. Dr. Oliver Stork, Prof. Dr. Anne Albrecht
Researchers: Dr.Gürsel Çalişkan
