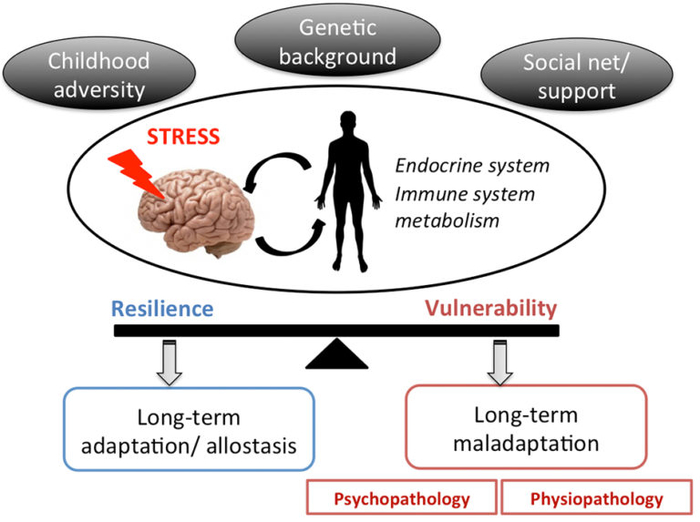
Stress
We are particularly interested in the mechanisms underlying traumatic stress-induced neuropsychiatric disorders. We have adopted a juvenile-stress induced model of post traumatic stress disorder and investigate the impact of juvenile adversity on neural circuit functions of amygdala and hippocampus as well as the underlying molecular mechanisms. Our data point towards a critical role of local GABAergic interneurons and GABA synthesis mechanisms in mediating the vulnerability to stress experience.
Selected Publications
Ardi Z, Richter-Levin A, Xu L, Cao X, Volkmer H, Stork O, Richter-Levin G. The role of the GABAA receptor Alpha1 subunit in the ventral hippocampus in stress resilience. Sci Rep 2019; doi: org/10.1038/s41598-019-49824-4.
Ivens S, Çalışkan G, Papageorgiou I, Cesetti T, Malich A, Kann O, Heinemann U, Stork O, Albrecht A. Persistent increase in ventral hippocampal long-term potentiation by juvenile stress: A role for astrocytic glutamine synthetase. Glia 2019; doi: 10.1002/glia.23683.
Richter-Levin G, Stork O, Schmidt MV. Animal models of PTSD: a challenge to be met. Mol Psychiatry 2019; 24(8):1135-1156
Saha R, Kriebel M, Volkmer H, Richter-Levin G, Albrecht A. A Neurofascin Knock Down in the Basolateral Amygdala Mediates Resilience of Memory and Plasticity in the Dorsal Dentate Gyrus Under Stress. Mol Neurobiol 2018; 55(9):7317-7326.
Albrecht A, Müller I, Ardi Z, Çalışkan G, Gruber D, Ivens S, Segal M, Behr J, Heinemann U, Stork O, Richter-Levin G. Neurobiological consequences of juvenile stress: A GABAergic perspective on risk and resilience. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2017 Mar;74(Pt A):21-43.
Funding
